Search Result
Results for "
Bacterial transcription
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
5
Biochemical Assay Reagents
2
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W045071
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
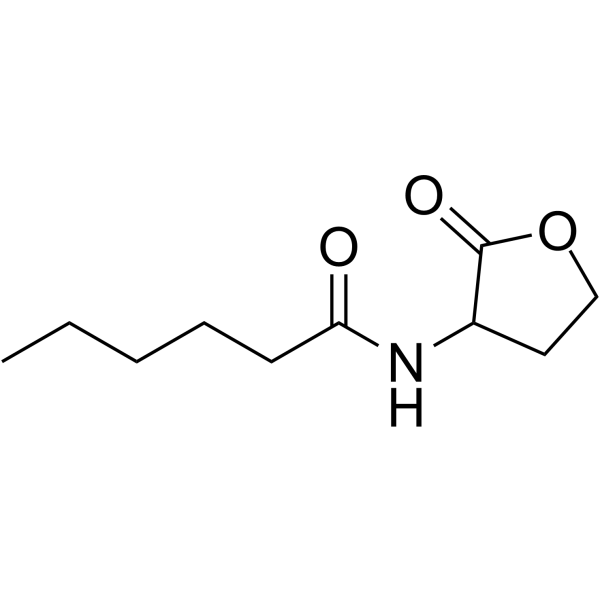
N-Hexanoyl-DL-homoserine lactone is a bacterial quorum sensing molecule produced in the rhizosphere. N-Hexanoyl-DL-homoserine lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing signal, induces transcriptional changes in Arabidopsis and may contribute to tuning plant growth to the microbial composition of the rhizosphere .
|
-
-
- HY-W004924
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
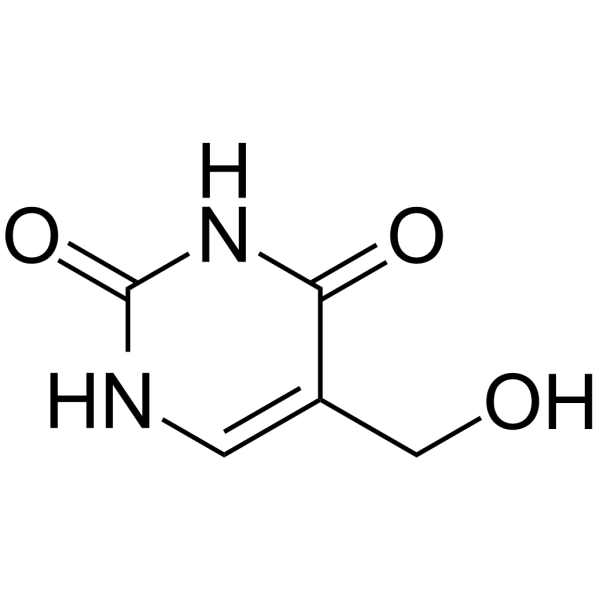
5-Hydroxymethyluracil is a product of oxidative DNA damage. 5-Hydroxymethyluracil can be used as a potential epigenetic mark enhancing or inhibiting transcription with bacterial RNA polymerase.
|
-
-
- HY-W040201
-
|
3-[3-(Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonate
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
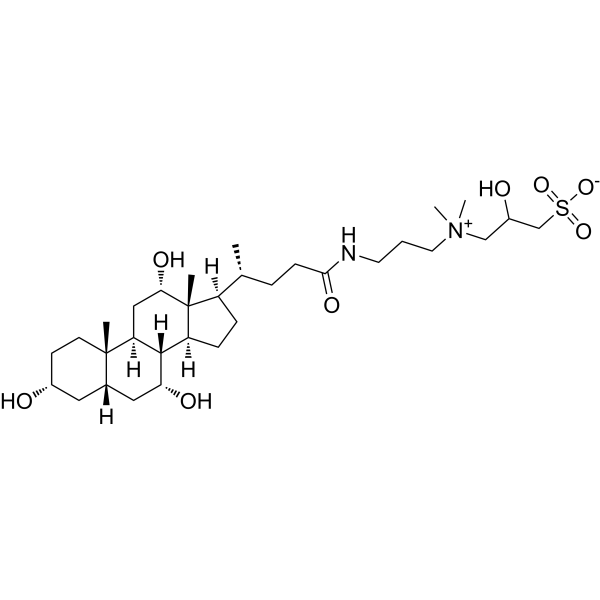
CHAPSO is a zwitterionic detergent that is thermally stable. CHAPSO is able to broaden the particle orientation distribution, enabling single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to produce isotropically uniform maps. CHAPSO can eliminate the directional bias of bacterial transcription complexes and help determine the structure of bacterial transcription complexes under cryo-electron microscopy .
|
-
-
- HY-146722
-
|
|
Bacterial
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
|
|
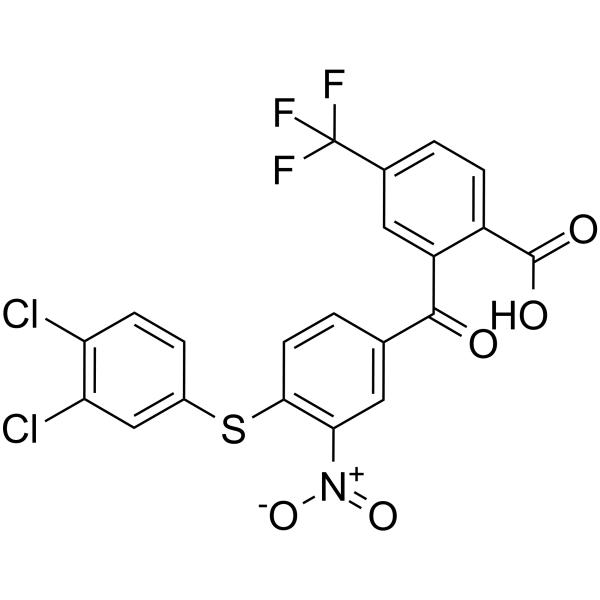
Antibacterial agent 89 is a potent antibacterial agent. Antibacterial agent 89 shows anti-clostridial activity. Antibacterial agent 89 inhibits the release of cytotoxins and the β’CH-σ interaction. Antibacterial agent 89 disrupts the process of bacterial transcription .
|
-
-
- HY-157130
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
T3SS-IN-3 (compound F-24) is an inhibitor of type III secretion system (T3SS). T3SS-IN-3 inhibits the transcription of hrpY gene significantly without inhibiting bacterial growth .
|
-
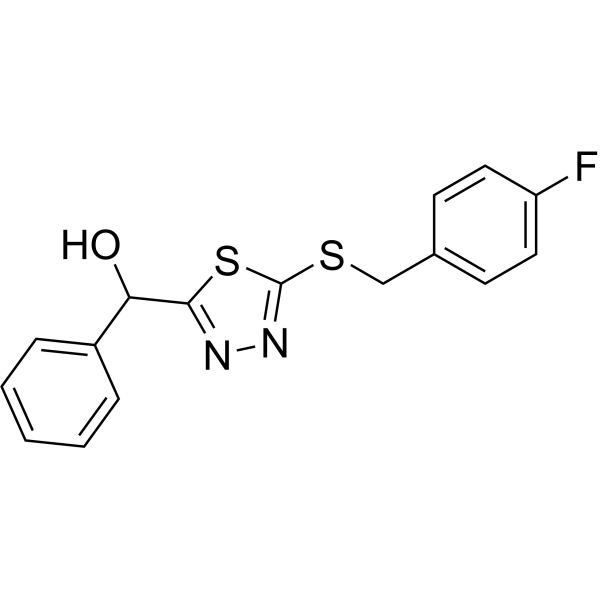
-
- HY-W004924S
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
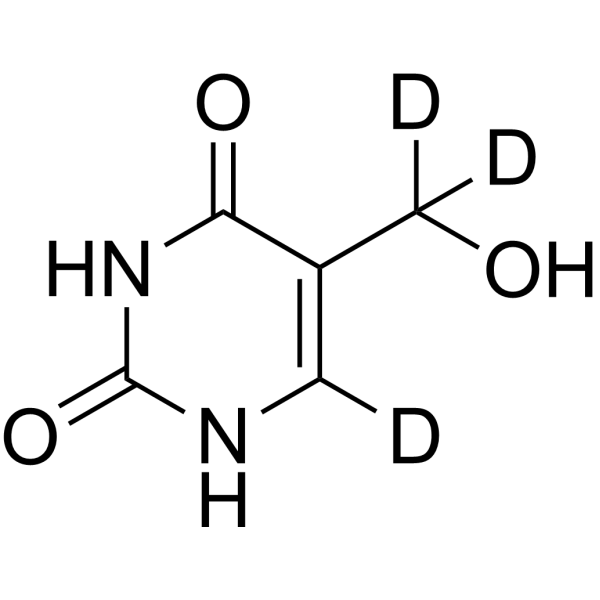
5-Hydroxymethyluracil-d3 is the deuterium labeled 5-Hydroxymethyluracil[1]. 5-Hydroxymethyluracil is a product of oxidative DNA damage. 5-Hydroxymethyluracil can be used as a potential epigenetic mark enhancing or inhibiting transcription with bacterial RNA polymerase[2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-116762
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
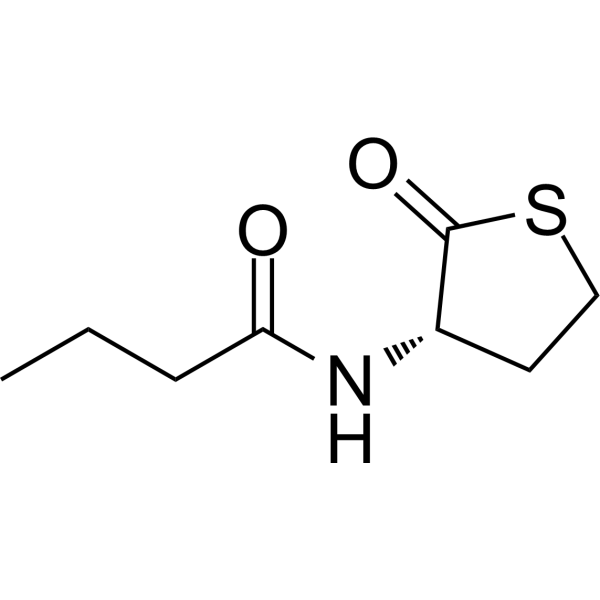
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. The control of bacterial infection by quenching the quorum sensing system of bacteria is a promising research area. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR protein family, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, a small, diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism . N-butyryl-L-homocysteine thiolactone induces violacein expression in Viola viola mutants that normally fail to produce AHL.
|
-
-
- HY-B1422
-
|
Aminacrine
|
Bacterial
HIV
|
Infection
|
|
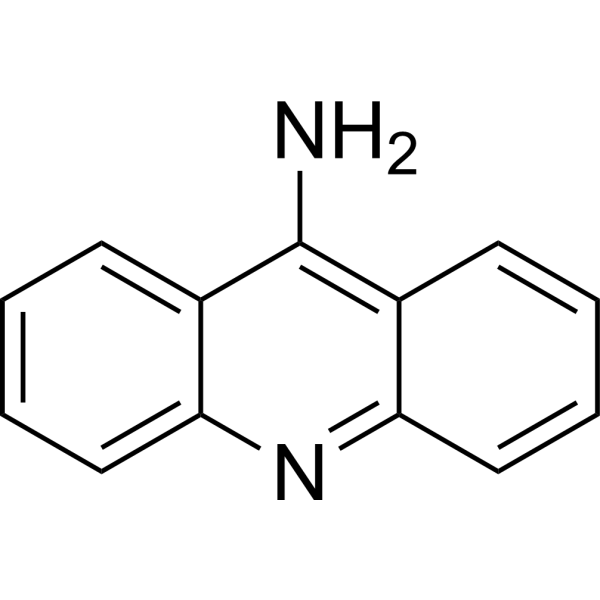
9-Aminoacridine, a fluorescent probe, acts as an indicator of pH for quantitative determination of transmembrane pH gradients (inside acidic). 9-Aminoacridine is an antimicrobial. 9-Aminoacridine exerts its antimicrobial activity by interacting with specific bacterial DNA and disrupting the proton motive force in K. pneumoniae. 9-Aminoacridine is a HIV-1 inhibitor and inhibits HIV LTR transcription highly dependent on the presence and location of the amino moiety. 9-Aminoacridine inhibits virus replication in HIV-1 infected cell lines. 9-Aminoacridine is used as a Rifampin (RIF; HY-B0272) adjuvant for the multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infections .
|
-
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
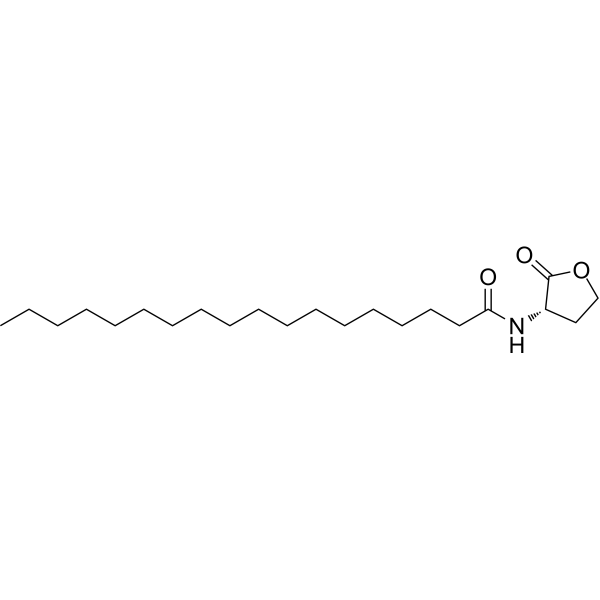
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
-
-
- HY-B1422S
-
|
Aminacrine-13C6
|
Bacterial
HIV
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Infection
|
|
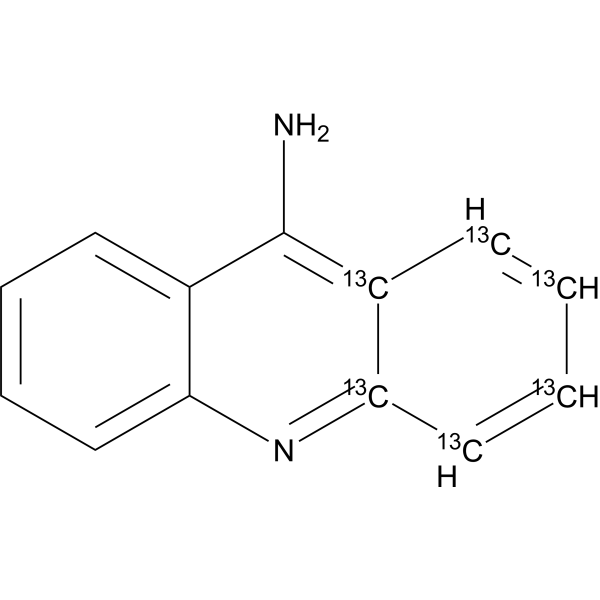
9-Aminoacridine-13C6 is the 13C-labeled 9-Aminoacridine(HY-B1422). 9-Aminoacridine, a fluorescent probe, acts as an indicator of pH for quantitative determination of transmembrane pH gradients (inside acidic). 9-Aminoacridine is an antimicrobial. 9-Aminoacridine exerts its antimicrobial activity by interacting with specific bacterial DNA and disrupting the proton motive force in K. pneumoniae. 9-Aminoacridine is a HIV-1 inhibitor and inhibits HIV LTR transcription highly dependent on the presence and location of the amino moiety. 9-Aminoacridine inhibits virus replication in HIV-1 infected cell lines. 9-Aminoacridine is used as a Rifampin (RIF; HY-B0272) adjuvant for the multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infections .
|
-
-
- HY-114773
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
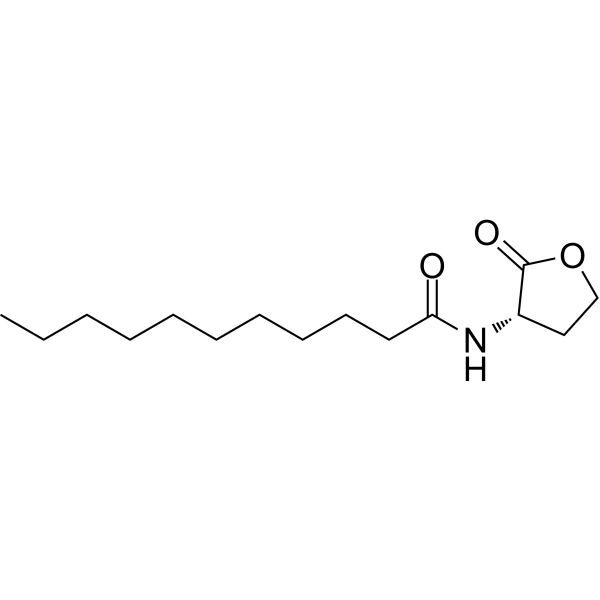
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C11-HSL has a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain and may be a minor quorum-sensing signaling molecule in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
|
-
-
- HY-W127393
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
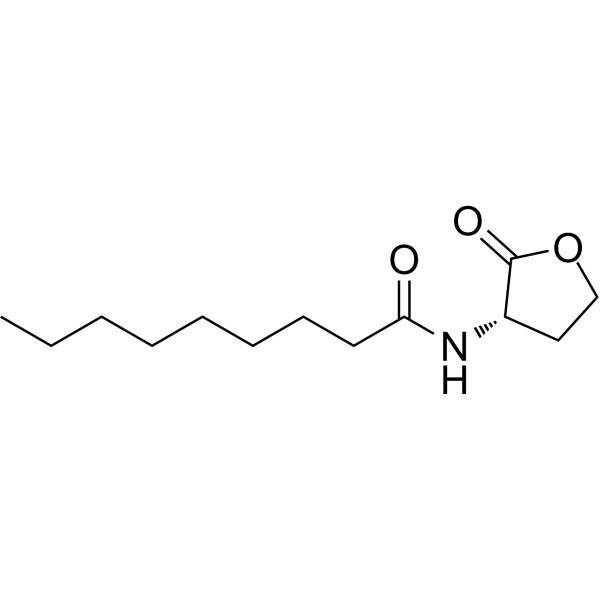
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C9-HSL is a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain produced by wild-type Erwinia carotovora strain SCC 3193 grown in nutrient-rich Luria-Bertani broth (LB) medium.
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-B1422
-
|
Aminacrine
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
9-Aminoacridine, a fluorescent probe, acts as an indicator of pH for quantitative determination of transmembrane pH gradients (inside acidic). 9-Aminoacridine is an antimicrobial. 9-Aminoacridine exerts its antimicrobial activity by interacting with specific bacterial DNA and disrupting the proton motive force in K. pneumoniae. 9-Aminoacridine is a HIV-1 inhibitor and inhibits HIV LTR transcription highly dependent on the presence and location of the amino moiety. 9-Aminoacridine inhibits virus replication in HIV-1 infected cell lines. 9-Aminoacridine is used as a Rifampin (RIF; HY-B0272) adjuvant for the multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infections .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-W040201
-
|
3-[3-(Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonate
|
Surfactants
|
|
CHAPSO is a zwitterionic detergent that is thermally stable. CHAPSO is able to broaden the particle orientation distribution, enabling single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to produce isotropically uniform maps. CHAPSO can eliminate the directional bias of bacterial transcription complexes and help determine the structure of bacterial transcription complexes under cryo-electron microscopy .
|
-
- HY-116762
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. The control of bacterial infection by quenching the quorum sensing system of bacteria is a promising research area. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR protein family, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, a small, diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism . N-butyryl-L-homocysteine thiolactone induces violacein expression in Viola viola mutants that normally fail to produce AHL.
|
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
-
- HY-114773
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C11-HSL has a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain and may be a minor quorum-sensing signaling molecule in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
|
-
- HY-W127393
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C9-HSL is a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain produced by wild-type Erwinia carotovora strain SCC 3193 grown in nutrient-rich Luria-Bertani broth (LB) medium.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-W004924S
-
|
|
|
5-Hydroxymethyluracil-d3 is the deuterium labeled 5-Hydroxymethyluracil[1]. 5-Hydroxymethyluracil is a product of oxidative DNA damage. 5-Hydroxymethyluracil can be used as a potential epigenetic mark enhancing or inhibiting transcription with bacterial RNA polymerase[2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-B1422S
-
|
|
|
9-Aminoacridine-13C6 is the 13C-labeled 9-Aminoacridine(HY-B1422). 9-Aminoacridine, a fluorescent probe, acts as an indicator of pH for quantitative determination of transmembrane pH gradients (inside acidic). 9-Aminoacridine is an antimicrobial. 9-Aminoacridine exerts its antimicrobial activity by interacting with specific bacterial DNA and disrupting the proton motive force in K. pneumoniae. 9-Aminoacridine is a HIV-1 inhibitor and inhibits HIV LTR transcription highly dependent on the presence and location of the amino moiety. 9-Aminoacridine inhibits virus replication in HIV-1 infected cell lines. 9-Aminoacridine is used as a Rifampin (RIF; HY-B0272) adjuvant for the multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infections .
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent:




















